Today’s interconnected world has transformed supply chain management into a data-driven field. While technology has improved transparency and efficiency, it has also raised data privacy and security concerns. Businesses must find a balance between utilizing data and protecting it from cyber threats.
Supply chain data availability, confidentiality, and integrity are critical for upholding stakeholder confidence and guaranteeing continuous company operations. Businesses utilize various data assets susceptible to cyber attacks, breaches, and other criminal activities. These data assets include proprietary product designs, customer information, financial transactions, and operational details. Thus, putting strong data security measures in place is crucial to defend against cyberattacks and illegal access.
- Get to Know Data Privacy Regulations: GDPR and CCPA
- Ensuring Data Privacy Regulations Compliance for Supply Chains
Data privacy is essential for protecting individuals from data breaches and their potential consequences. Companies must collect, use, and share personal information responsibly, ensuring transparency and safeguarding against unauthorized access. Trust between businesses and their customers hinges on solid data privacy practices.
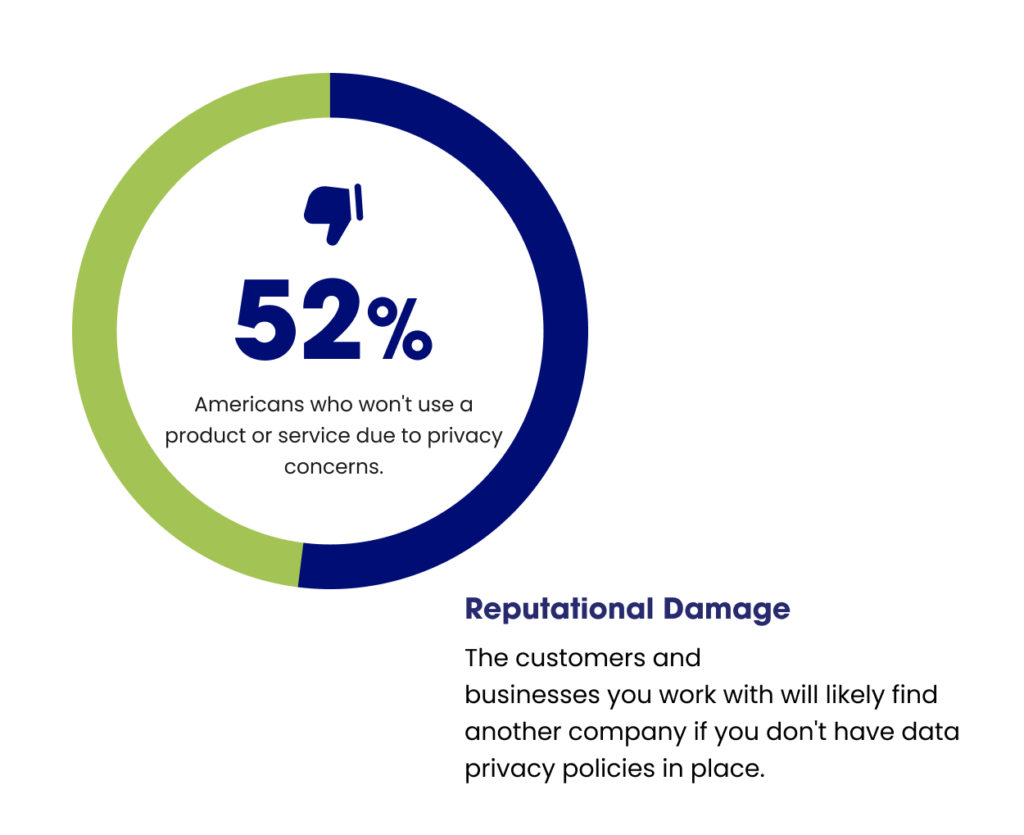
In recent years, however, consumer confidence has been affected by high-profile data breaches. According to a Wakefield Research study, 87% of customers will cut ties with a company if they have doubts about its data security procedures. Another 60% of consumers think that dangers to their personal information are expanding faster than organizations can handle.
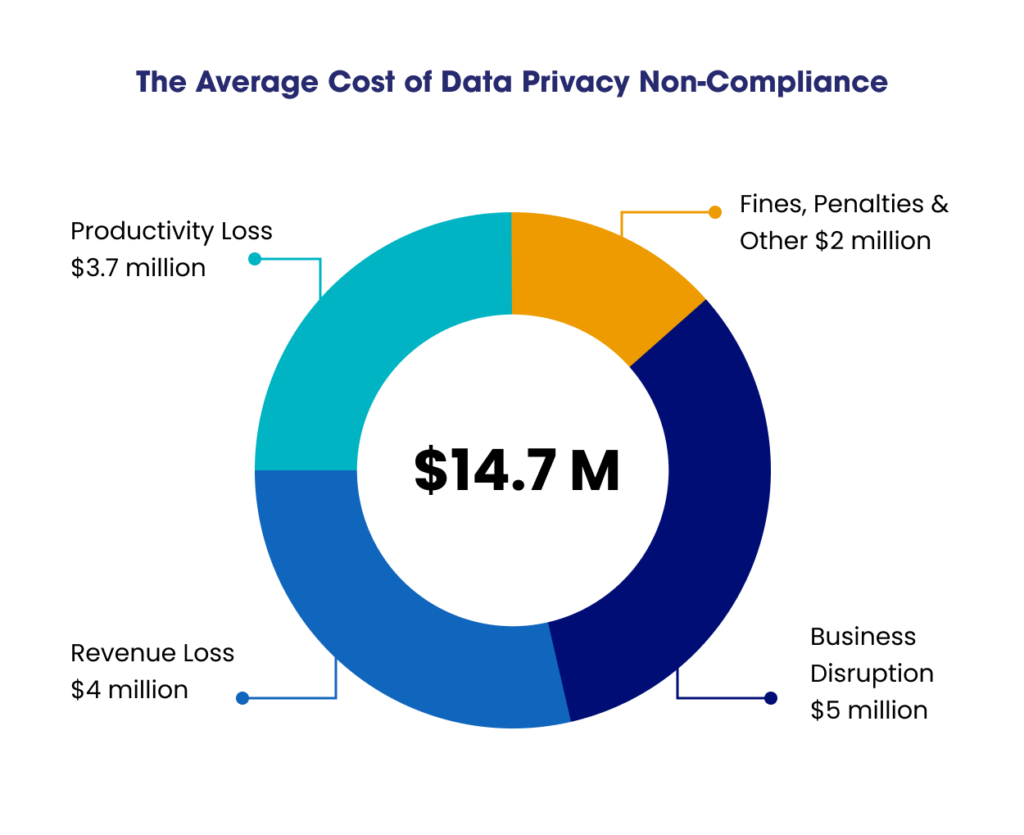
Cyberattacks and data breaches have led to legislation imposing stricter data privacy regulations with harsh penalties for noncompliance. Companies can lose almost three times as much due to data breaches and regulatory violations as they would from preventative compliance efforts.
According to a Wakefield Research study, 87% of customers will cut ties with a company if they have doubts about its data security procedures. Another 60% of consumers think that dangers to their personal information are expanding faster than organizations can handle.
Get to Know the Data Privacy Regulations: GDPR and CCPA
The enactment of the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR) by the EU in 2018 and the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) by California in 2020 stressed the importance of data privacy regulations. These two regulations set the standard for data privacy and protection in the era of digital sharing.
In theory, data protection laws are also data sovereignty legislation. Their goal is to provide appropriate security for individuals’ private data. Data privacy regulations require any personal information kept in a particular area to be governed by the data protection laws enforced in the region. For example, data held in Europe will be governed by the General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR), the European Union’s current data protection regulation.
The General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR)
The GDPR is a comprehensive data privacy law that applies to all organizations that gather, store, or handle the personal data of individuals living in the European Union. It regulates how companies collect, use, keep, and transmit the data of EU individuals to safeguard their privacy. Firms outside of the EU that collect, use, or keep the personal data of EU citizens are also subject to this privacy rule.
The GDPR requires logistics and supply chain companies to have a lawful reason for collecting, storing, or using customer data. This data must be necessary for specific purposes, like fulfilling contracts or complying with laws. Companies should only request data that is essential for their services.
All logistics and supply chain organizations must also notify their clients of any data breaches within 72 hours of the violation. This gives data subjects enough time to take the necessary precautions to protect themselves from potential repercussions.
Supply chain companies that violate any of the aforementioned requirements or these data privacy regulations will face severe fines. Under the GDPR, a company may be fined up to €20 million, or 4% of its yearly worldwide sales.
California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA)
With federalism implemented in the U.S., states can adopt data privacy regulations to safeguard their citizens. The CCPA is a state-level data protection statute created to defend the data rights of residents of California, USA. Whether or not a business is headquartered in the U.S., firms must abide by these regulations if they gather, use, or keep the personal data of California residents.
The CCPA extends its reach to supply chain and logistics organizations, mandating transparency in data collection practices. Businesses must disclose how they gather, utilize, and safeguard customer data, including shipment information shared with carriers and partners. The law also prohibits discrimination against customers who exercise their CCPA rights, such as refusing the sale of personal data or demanding alternative rates.
Supply chain and logistics companies must implement robust data privacy policies and procedures. Customers should have clear mechanisms to exercise their rights, and any third-party data sharing must adhere to relevant regulations. Failure to comply with the CCPA can result in significant fines and penalties enforced by the California Attorney General’s office.
Ensuring Data Privacy Regulations Compliance for Supply Chains
Data privacy regulations protect people’s personal information from abuse or improper handling. These restrictions can significantly impact businesses, particularly those that conduct business internationally. Ensuring compliance with data privacy standards is essential to avoid potential fines and penalties.
Data protection challenges in the logistics industry
While data security is essential, certain elements make compliance difficult in logistics. Here are the challenges:
Multiple stakeholders in the supply chain
A supply chain involves multiple stakeholders, including carriers, warehouses, suppliers, manufacturers, and consumers. Its logistics can be complex, especially when managing data that flows between various systems and entities within this intricate ecosystem.
Data security risks
Logistics operations encompass transporting and storing goods, often involving sharing sensitive information like tracking numbers, product details, and delivery addresses. Data breaches and unauthorized access are a significant concern, particularly during transit and storage.
Transferring data in cross-border operations
Cross-border supply chain operations involve the movement of goods across national borders and the transfer of personal data. Navigating the legal and regulatory frameworks governing these cross-border data transfers can be complex. Supply chain managers must be mindful of data sovereignty and localization requirements.
The complexity of global supply chains
Supply chains are becoming increasingly intricate, with complex networks connecting multiple tiers of suppliers and subcontractors. Limited visibility and control over subcontractors and third-party service providers can hinder the enforcement of data protection and security measures throughout the supply chain.
Various data privacy laws
Logistics companies are subject to various data privacy regulations, including the GDPR and CCPA. Compliance can be challenging due to varying data sovereignty laws across different jurisdictions, making it difficult for some businesses to adhere to all applicable regulations.
Staying compliant with data privacy regulations
Companies must establish a clear structure to ensure third-party suppliers manage data appropriately. Communication and visibility must be prioritized to adhere to data privacy legislation and minimize non-compliance risks.
Clearly explain the guidelines for data gathering.
Companies should clearly define the data that will be exchanged and its intended uses to prevent information abuse or illegal sharing. Additionally, companies should require vendors to submit regular reports on their data handling practices and any potential security incidents or breaches.
Suppliers must shoulder data protection responsibilities.
When a business shares data management with suppliers or logistic partners, it loses control over the data. Contracts should be drafted with explicit indemnity terms that make the provider liable for violations or non-compliance.
Enforce data security standards with suppliers.
Contractual terms can require suppliers to maintain security-related measures like encryption and access restrictions. Comprehensive cybersecurity insurance is also a great way to protect data privacy, safeguarding the primary business and its customers in case of a security breach.
Transparency with third-party partners
Large-scale suppliers often rely on subcontractors, which can lengthen supply chains and increase the risk of regulatory breaches or data security incidents. Contracts should include provisions requiring suppliers to ensure their subcontractors adhere to the same data protection standards. Additionally, businesses should carefully evaluate potential subcontractors’ capabilities and compliance practices before entering into agreements.
Suppliers audits to guarantee compliance
Firms should audit their suppliers and subcontractors to ensure they adhere to data security rules. These audits, carried out by a third party, assess the efficacy of current policies. They can spot any contract non-compliance concerns with suppliers, strengthen controls, and lower the possibility of data security lapses or breaches.
Conclusion
Data privacy and cybersecurity are paramount as supply chains become more digitally integrated. Organizations must proactively tackle these difficulties and guarantee supply chain integrity.
By adopting a comprehensive strategy, businesses can tackle the challenges of supply chain management while protecting sensitive data and upholding stakeholder confidence. A mix of technical solutions, organizational practices, and cooperative efforts bolsters compliance with data privacy regulations. The key to ensuring supply chain resilience in the future is to strike a balance between data-driven operations and safeguarding security and privacy.
Aratum helps you comply with data privacy regulations. Our supply chain software allows you to manage supplier relationships and digitize transactions. Book a demo to experience how easy it is to use our console.
The featured photo of this article was sourced from rawpixel.com on Freepik



